Warning Signs of an Incoming Stroke
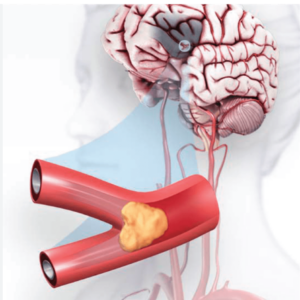
A stroke, also known as a cerebrovascular accident (CVA), is a life-threatening emergency that occurs when the blood flow to a part of the brain is interrupted or reduced. Without enough oxygen and nutrients, brain cells begin to die, leading to permanent damage if not treated promptly. Early recognition of stroke warning signs can help save lives and minimize brain damage.
READ MORE: Whitehead Inflammatory Acne
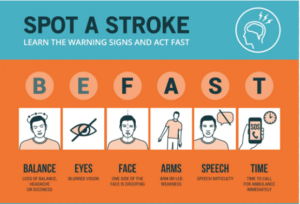
Warning Signs
- Sudden Weakness or Numbness on One Side of the Body
One of the most obvious signs of a stroke is sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body, including the face, arms, or legs. The person may find it difficult to move or speak, or they may lose sensation in part of their body. - Difficulty Speaking or Slurred Speech
Another sign is the inability to speak clearly or slurred speech. This can happen when the stroke affects the part of the brain responsible for language. If you notice someone having trouble speaking or unable to speak at all, it could be a sign of a stroke. - Blurred Vision or Sudden Loss of Vision
A stroke can affect vision, causing blurred or sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes. This happens due to the disruption of blood flow to the area of the brain that controls vision. - Sudden Severe Headache
A sudden, severe headache that feels much worse than a typical headache can be a sign of a stroke, particularly if it’s accompanied by nausea or vomiting. This is a symptom that requires immediate emergency care. - Loss of Balance or Dizziness
A stroke can cause significant dizziness, a feeling of imbalance, or difficulty walking. The person may feel as though they are losing their sense of direction or unable to stand. - Sudden Difficulty Breathing
Sudden shortness of breath can be a warning sign of a stroke, especially when accompanied by other symptoms like numbness, muscle weakness, or difficulty communicating. This indicates that the brain may not be receiving enough oxygen due to a blockage or reduced blood flow. - Sudden Changes in Mood or Behavior
A stroke can cause abrupt changes in a person’s emotions and behavior, such as losing the ability to think clearly or losing control over emotions. The person may feel confused, anxious, or easily irritated for no apparent reason. - READ MOER: 3 Harmful Sleeping Habits to Avoid for Better Health
What to Do If You or Someone Else Shows Stroke Symptoms?
- Call Emergency Services Immediately: If you notice any signs of a stroke, the most important thing is to call emergency services right away. Time is critical, and prompt intervention can help minimize brain damage.
- Do Not Let the Person Eat or Drink: If you suspect someone is having a stroke, do not allow them to eat or drink while waiting for emergency services to arrive. This can complicate treatment if surgery or medical intervention is necessary.
- Record the Time Symptoms Started: Keep track of the exact time the symptoms first appeared. This information is crucial for doctors to determine the best treatment options.
Why Time Matters in Stroke Treatment?
Every minute counts when a stroke occurs. Brain cells begin to die rapidly due to a lack of oxygen and nutrients. Treatment within the first 3-4.5 hours of a stroke can significantly reduce brain damage and improve recovery outcomes. The quicker the intervention, the higher the chances of saving the patient’s life and restoring function.
How to Prevent a Stroke
- Maintain Healthy Blood Pressure: High blood pressure is a major risk factor for strokes. Regularly check your blood pressure and keep it within a healthy range to reduce the risk of stroke.
- Follow a Healthy Diet: Eat plenty of vegetables, fruits, and high-fiber foods, and limit the intake of foods high in salt and saturated fats.
- Exercise Regularly: Engaging in regular physical activity helps maintain cardiovascular health, control weight, and reduce the risk of stroke.
- Control Cholesterol Levels: High cholesterol levels can increase the risk of stroke. Regularly monitor your cholesterol and adjust your diet accordingly.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of stroke. Quitting smoking is a vital step in protecting cardiovascular health and lowering stroke risk.
- Manage Stress: Stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or relaxation exercises can help lower the risk of stroke by reducing stress-related effects on the body.
Conclusion
A stroke is a serious condition but one that can be prevented with early identification of warning signs. If you or someone around you shows symptoms of a stroke, do not hesitate—call emergency services immediately. Acting quickly can save lives and reduce permanent brain damage. Take care of your cardiovascular health and implement preventive measures to avoid strokes.