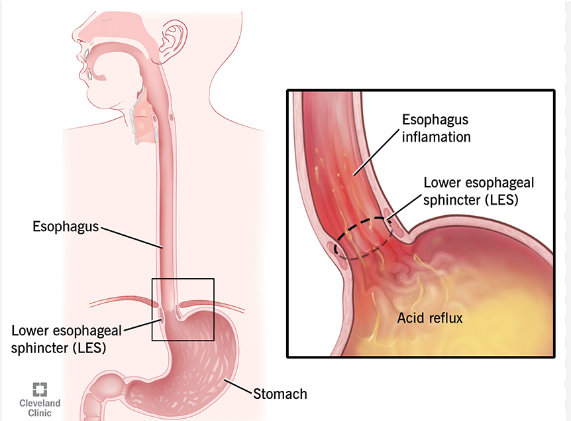
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) is a health condition that occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing discomfort and various symptoms. GERD can lead to serious issues if not treated in a timely manner.
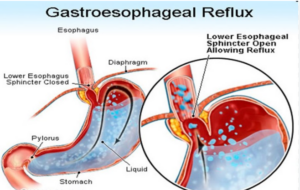
Causes of GERD:
- Weak Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES): This muscle prevents stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus. When the LES becomes weak or doesn’t function properly, acid can easily reflux into the esophagus.
- Smoking: Nicotine can weaken the function of the LES, making it easier for acid to flow back into the esophagus.
- Overweight or Obesity: Excess body weight can put pressure on the stomach, leading to acid reflux, especially when lying down or bending over.
- Consumption of Trigger Foods: Foods such as chocolate, coffee, spicy foods, and high-fat meals can increase the risk of acid reflux.
- Pregnancy: Pressure from the growing fetus can cause acid reflux, particularly in the later stages of pregnancy.
Symptoms of GERD:
- Heartburn: A burning sensation in the chest, often occurring after eating or lying down.
- Chest Pain: Pain that can last for a while and feel similar to a heart attack.
- Difficulty Swallowing: A sensation of something being stuck in the throat or esophagus.
- Dry Cough or Hoarseness: Especially in the morning.
- Bad Breath: When stomach acid refluxes, it can cause unpleasant breath odor.
- Nausea: A feeling of nausea or vomiting, particularly after meals.
Treatment for GERD:
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Lose weight if overweight.
- Avoid eating large meals before sleeping: Avoid eating at least 2-3 hours before going to bed.
- Elevate the head of the bed while sleeping: This helps prevent acid reflux when lying down.
- Avoid trigger foods: Such as spicy, acidic, or fatty foods.
- Medications:
- Acid inhibitors: Such as antacids, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), or H2 blockers.
- Stomach acid reducers: These help reduce the amount of acid in the stomach, thus reducing reflux.
- Surgery: In severe cases, when medications are ineffective, a doctor may recommend surgery to tighten the lower esophageal sphincter.
Note:
If GERD is not treated in a timely manner, it can lead to serious complications such as esophageal inflammation, narrowing of the esophagus, or an increased risk of esophageal cancer. If you experience persistent GERD symptoms, it’s important to consult a doctor for diagnosis and timely treatment.
Read more: How to know if you have Oral Thrush ???